Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to the SQL GROUP BY clause to group rows into a set of summary rows by the values of columns or expressions.
Introduction to SQL GROUP BY clause
The GROUP BY clause is used to group rows returned by SELECT statement into a set of summary rows or groups based on values of columns or expressions. You can apply an aggregate function such as SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX or COUNT to each group to output the summary information.
The GROUP BY clause is very useful when you want to analyze data in analytical fashion e.g., products were purchased by a customer or sold by a sale person by quarter. Therefore you often find the GROUP BY clause applied in the data warehouse and business intelligence (BI) systems to produce the analytical reports.
The typical syntax of GROUP BY is as follows:
SELECT
column1, column2, aggregate_function(expression)
FROM
table_name
WHERE
condition
GROUP BY column1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)SQL GROUP BY examples
Let’s take a look at the products table:
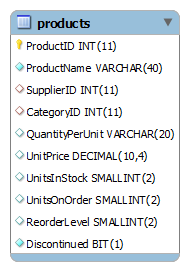
SQL GROUP BY with SUM function example
To get the total units in stock for each product category, you use the GROUP BY clause with the SUM function as follows:
SELECT
categoryid, SUM(unitsinstock)
FROM
products
GROUP BY categoryid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The database engine performs the following steps:
- First, examines the
GROUP BYclause and divides the products into groups based on the product categorycategoryid. - Second, calculates the total of units in stock by using the
SUMfunction for each group.
SQL GROUP BY with COUNT function example
The following query selects the number of products in each product category by using the GROUP BY clause with the COUNT function.
SELECT
categoryid, COUNT(productid)
FROM
products
GROUP BY categoryid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
SQL GROUP BY with AVG function
You can check the average number of units in stock for each product category by using the GROUP BY clause and AVG function as the following query:
SELECT
categoryid, FLOOR(AVG(unitsinstock))
FROM
products
GROUP BY categoryid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
The FLOOR function is used to get the largest integer value that is not greater than the argument.
SQL GROUP BY with MIN and MAX functions
Apply the same technique, you can select minimum and maximum units in stock for each product category as follows:
SELECT
categoryid, MIN(unitsinstock), MAX(unitsinstock)
FROM
products
GROUP BY categoryid;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)SQL GROUP BY with ORDER BY example
The GROUP BY clause is used in conjunction with the ORDER BY clause to sort the groups. For example, you can sort product categories by the number of products as the following query:
SELECT
categoryid, COUNT(productid)
FROM
products
GROUP BY categoryid
ORDER BY COUNT(productid) DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
SQL GROUP BY multiple columns
You can group the result set by not only one column but also multiple columns. For example, if you want to know how many sale orders that were ordered by a customer and sold by a sale person, you can group the result set based on both customer and sale person.
The database diagram of related tables is as follows:

The following query illustrates the idea:
SELECT
b.customerid,
b.CompanyName,
COUNT(a.orderid) AS 'Orders',
CONCAT(e.lastname, e.firstname) as 'Sale Person'
FROM
orders a
INNER JOIN customers b ON a.customerid = b.customerid
INNER JOIN employees e ON e.employeeid = a.employeeid
GROUP BY b.customerid,
a.employeeid
ORDER BY b.customerid ASC,
'Number of orders' DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the SQL GROUP BY clause to divide rows into groups and apply the aggregate function to each group to produce summary output.
