GridLayout places components in a cell of a grid. Each cell has the same size, therefore, each component takes up the same space in a container. When the user adjusts the container, the size of each component changes accordingly.
Here are the constructors of the GridLayout class:
| Constructors | Description |
|---|---|
| public GridLayout(int rows, int cols) | Creates a grid layout with a given number of rows and columns. If cols or rows is zero, any numbers of components can be placed in a column or in a row. |
| public GridLayout(int rows, int cols, int hgap, int vgap) | Creates a grid layout with a given number of rows and columns. Beside this, you can initialize the vertical and horizontal gap between each of rows and columns. |
Here is the screenshot of GridLayout demo application.
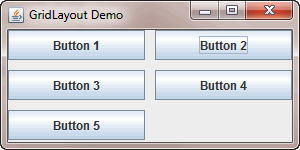
package gridlayoutdemo;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("GridLayout Demo");
JButton btn1 = new JButton("Button 1");
JButton btn2 = new JButton("Button 2");
JButton btn3 = new JButton("Button 3");
JButton btn4 = new JButton("Button 4");
JButton btn5 = new JButton("Button 5");
// create grid layout with 3 rows , 2 columns with horizontal
// and vertical gap set to 10
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(3,2,10,10));
// add buttons to the panel
panel.add(btn1);
panel.add(btn2);
panel.add(btn3);
panel.add(btn4);
panel.add(btn5);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,150);
frame.getContentPane().add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}Code language: JavaScript (javascript)